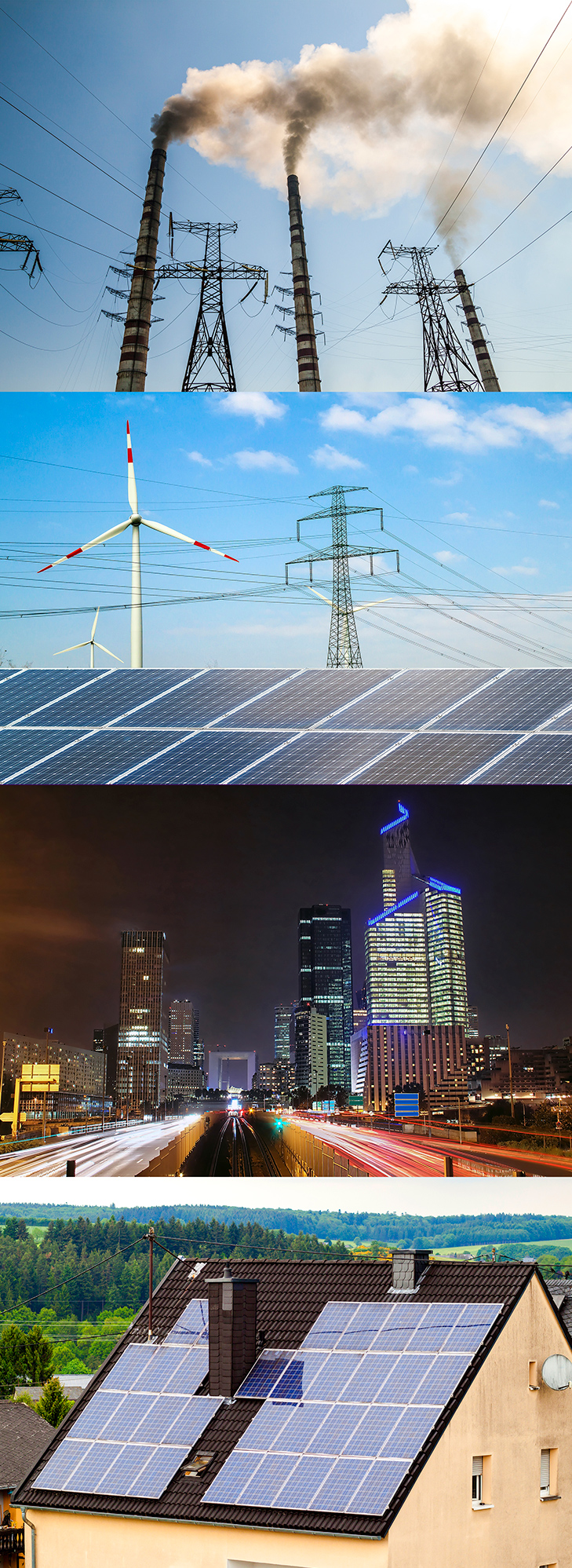
What is electricity?
Electricity is a natural force.
Scientists have determined that atoms consist of a nucleus of positively-charged particles they call protons and neutral particles called neutrons. Negatively-charged particles called electrons orbit around the nucleus. The electrons in an atom’s outermost shells can be pushed out of their orbits. Applying a force can make them shift from one atom to another. These shifting electrons are electricity.
Electricity is a secondary energy source that we get from the conversion of other sources of energy such as the sun or water-power or fossil fuels (coal, oil, natural gas).
How does America get its energy?
Wind, fossil fuel, solar: Get the facts on how America keeps its lights on. Our electric power sector, that is the utilities and companies that make electricity, is the biggest energy hog. It accounts for 34% of all energy use. But here’s the fact that surprised me: more than half of the energy consumed is lost in the process of getting that electricity to the consumer. Learn more.
Here are some fun facts about solar power…

Old Technology
Solar energy has been used for thousands of years. The ancient Greeks and Romans used passive solar design, building homes that captured sunlight for warmth

Fastest-Growing Energy Source
Solar power is currently the fastest-growing source of new energy. In the U.S., solar capacity has increased by over 35 times since 2008.

Enough to Power the Earth
The sun provides more energy to Earth in one hour than all of humanity uses in an entire year! If harnessed efficiently, solar energy could meet global energy needs many times over.

Solar-Powered Flights
The Solar Impulse 2, a solar-powered airplane, completed a flight around the world in 2016 without using a single drop of fuel.

Job Creator
Solar energy is a major job creator. In the U.S. alone, there are more jobs in the solar industry than in fossil fuel power plants.

Silent Power
Solar panels make no noise as they generate electricity, unlike traditional power plants which can be loud and polluting.

Solar Trees
Some cities and businesses are installing “solar trees,” which are structures that look like trees but have solar panels for leaves. They provide shade and generate electricity at the same time.
Here are some fun facts about electricity…
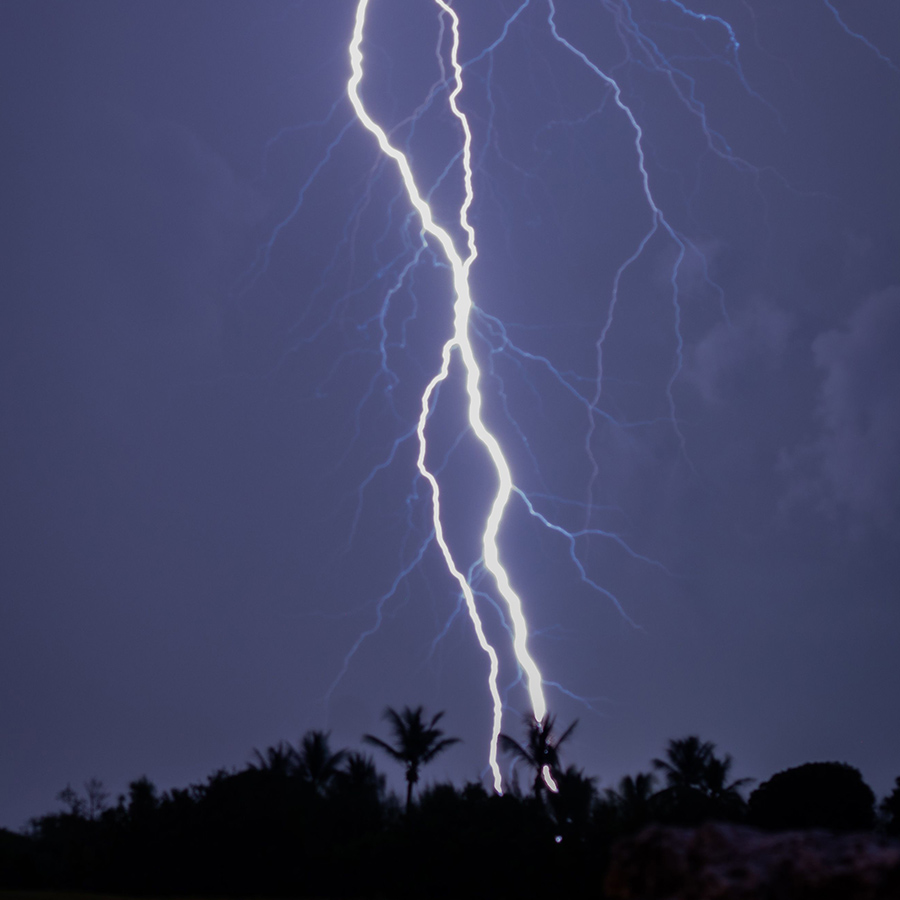

Lightning is Supercharged
A single bolt of lightning can carry up to 1 billion volts of electricity and heat the surrounding air to temperatures five times hotter than the surface of the sun!
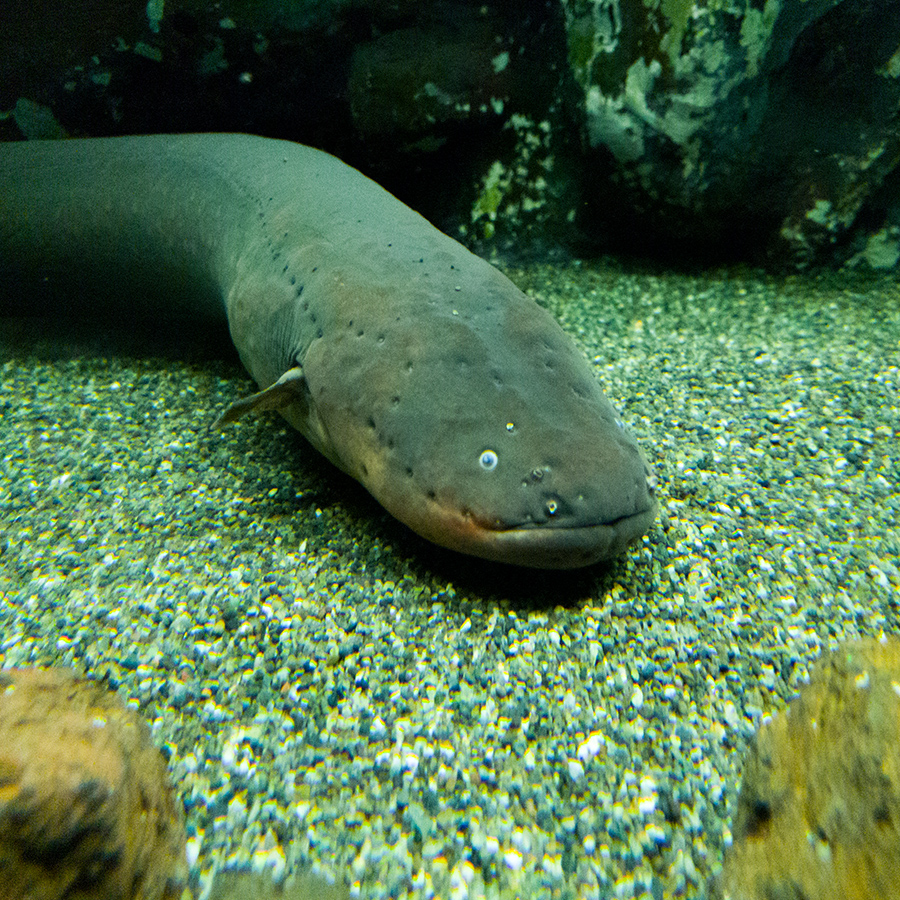

Electric Eels Generate Electricity
Electric eels can generate electricity to stun prey or defend against predators. They can release up to 600 volts of electricity!

Electricity Travels Fast
Electricity moves at nearly the speed of light—about 186,000 miles per second.
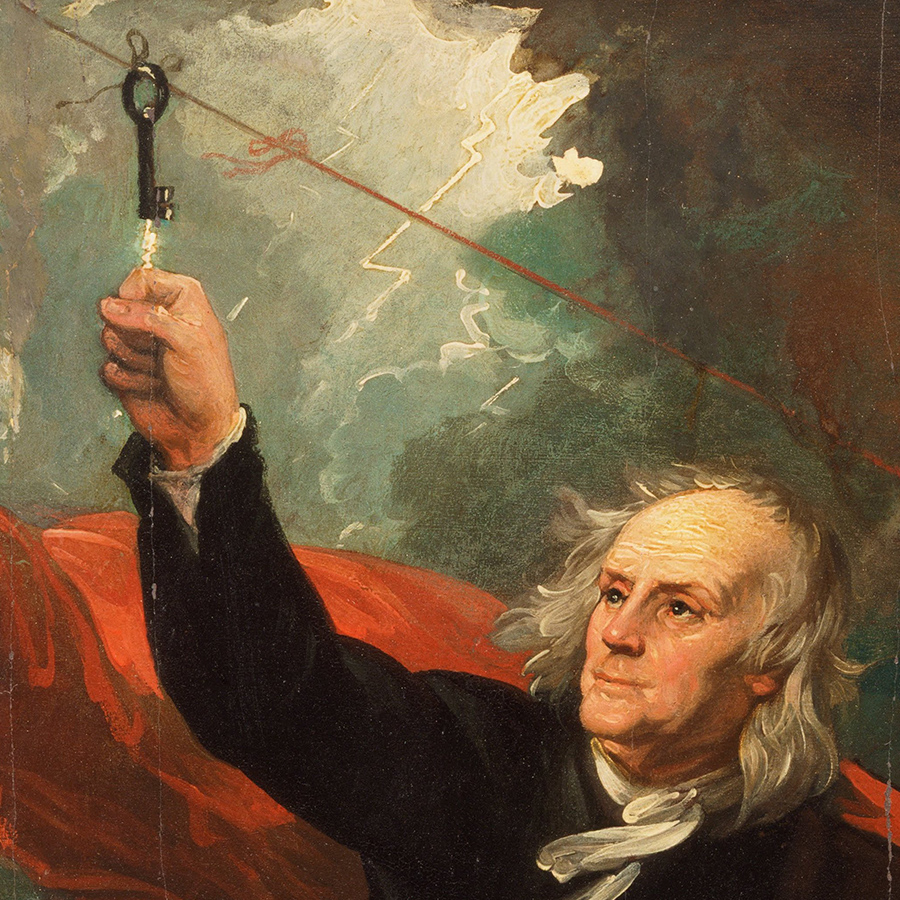

Benjamin Franklin Didn’t Discover Electricity
While Franklin’s famous kite experiment demonstrated the connection between lightning and electricity, people were aware of electricity long before, with ancient civilizations using it for rudimentary purposes.

The First Power Plant was installed in 1879
The First Power Plant was installed in 1879 at the Brush Electric Company, founded by Charles F. Brush, an inventor and pioneer in electrical engineering. Brush’s dynamos were used to power arc lamps for street lighting, marking one of the earliest uses of electricity for public lighting in the United States. Cleveland became the first city to have electric streetlights, starting with a section of Public Square.
Electricity and the Human Body
Our bodies rely on electricity to function. Nerve cells communicate with each other using electrical impulses, helping control muscles and the brain’s activity.
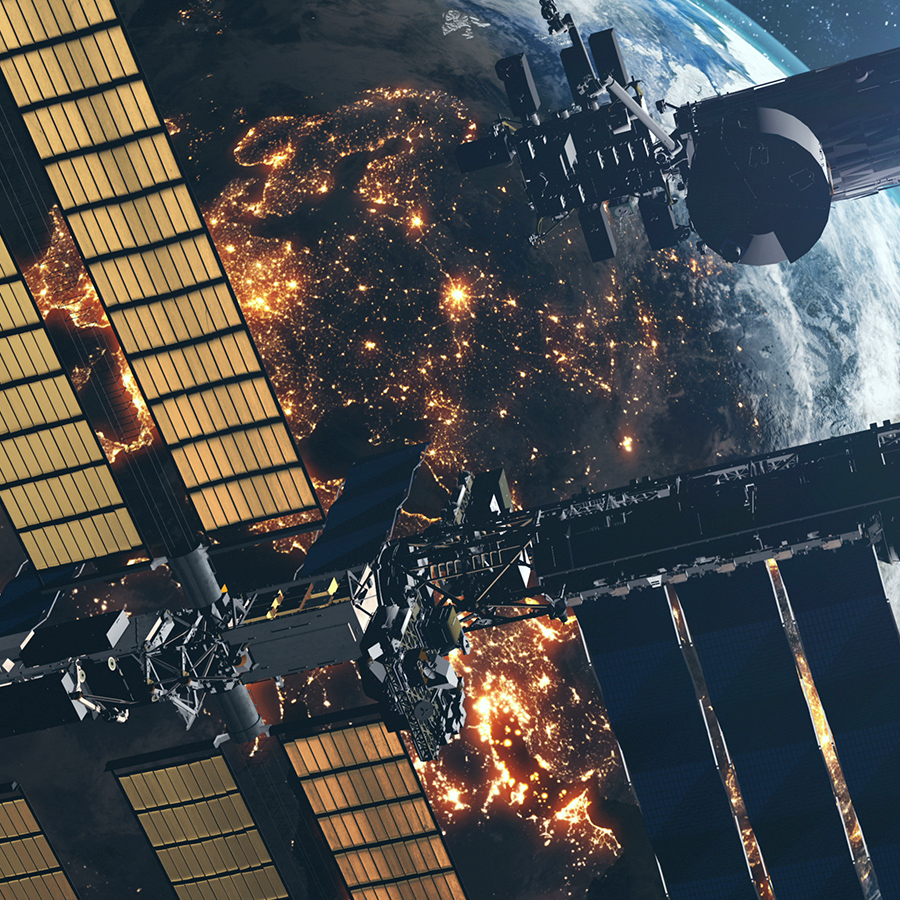

Electricity in Space
Astronauts on the International Space Station use solar panels to convert sunlight into electricity, which powers all the station’s systems.
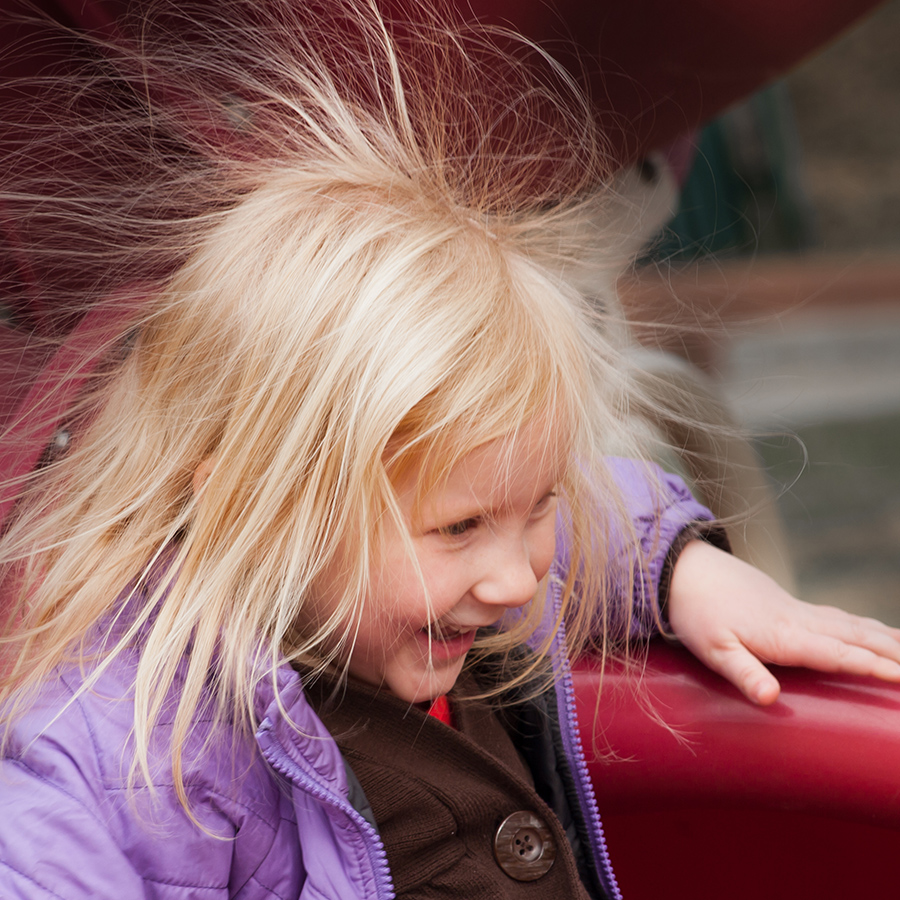

Static Electricity
When you rub a balloon on your hair, the static electricity causes your hair to stand up because similar electric charges repel each other.
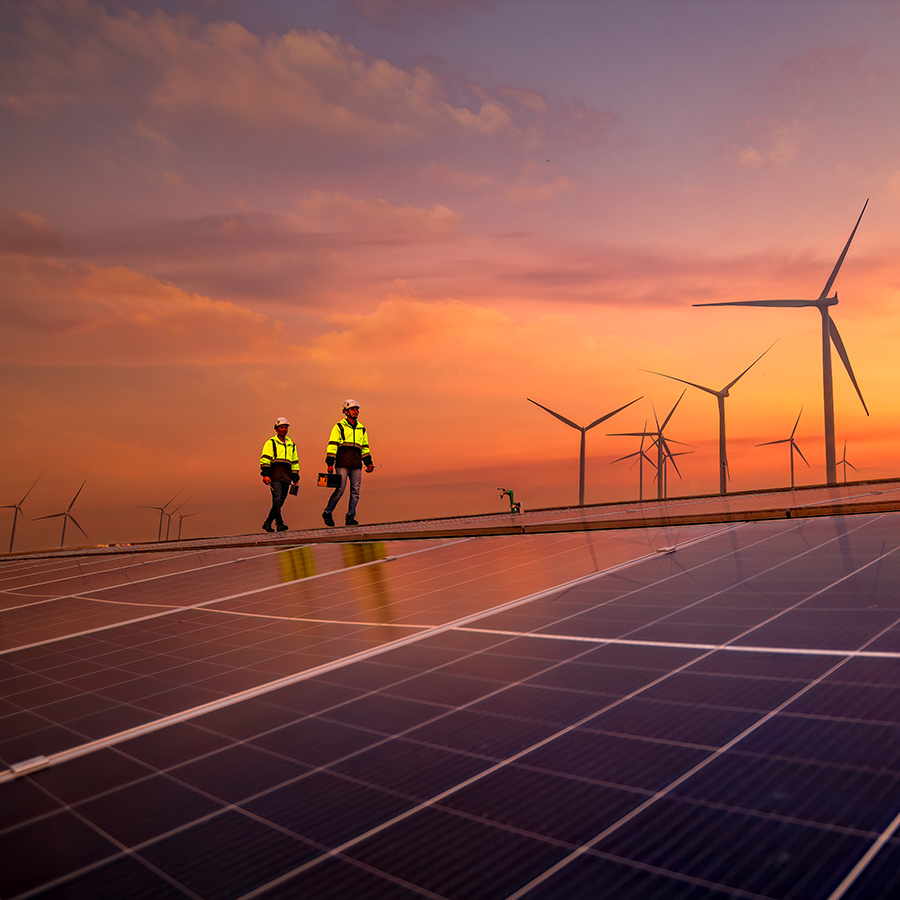

Renewable Electricity
The world is rapidly transitioning to renewable electricity sources like wind, solar, and hydroelectric power, which now generate about 28% of global electricity as of 2023.
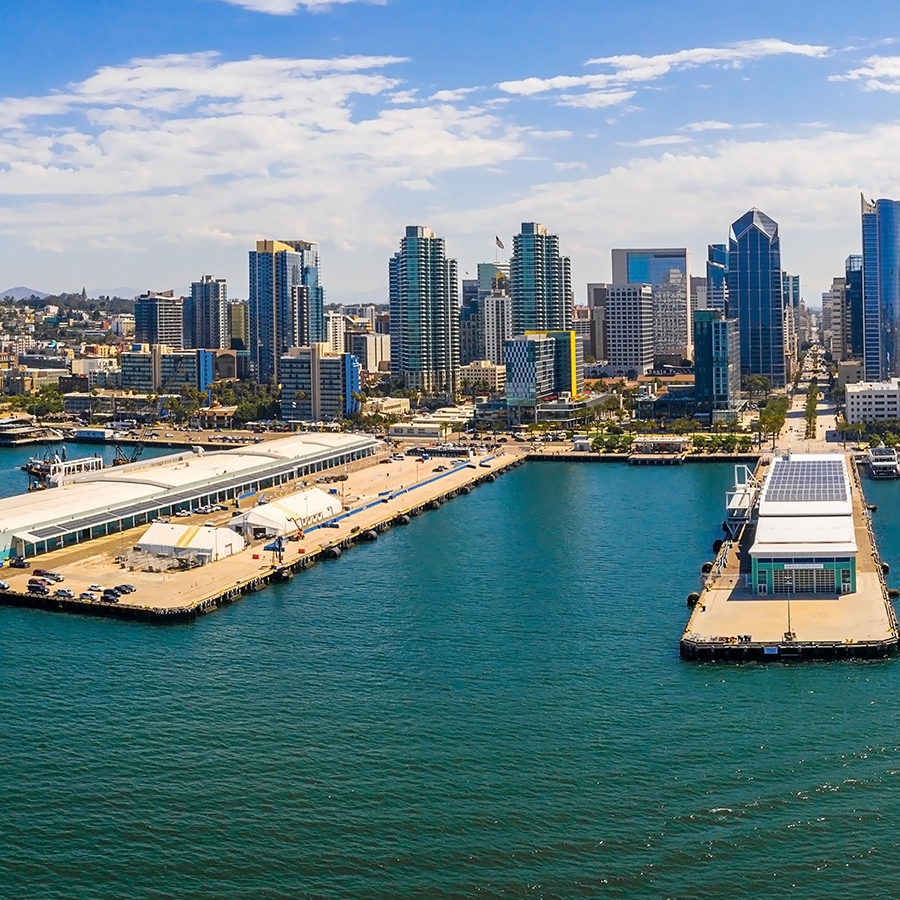

Naval facilities in San Diego consume a significant amount of electricity particularly given the presence of large installations like Naval Base San Diego, one of the largest Navy surface ship bases on the West Coast. Recent projects to enhance the region’s electrical infrastructure aim to improve energy efficiency and reduce emissions. For instance, the Navy’s ongoing electrification and energy efficiency projects are helping reduce their carbon footprint, potentially generating up to $20 million annually in value from low-carbon fuel credits.
